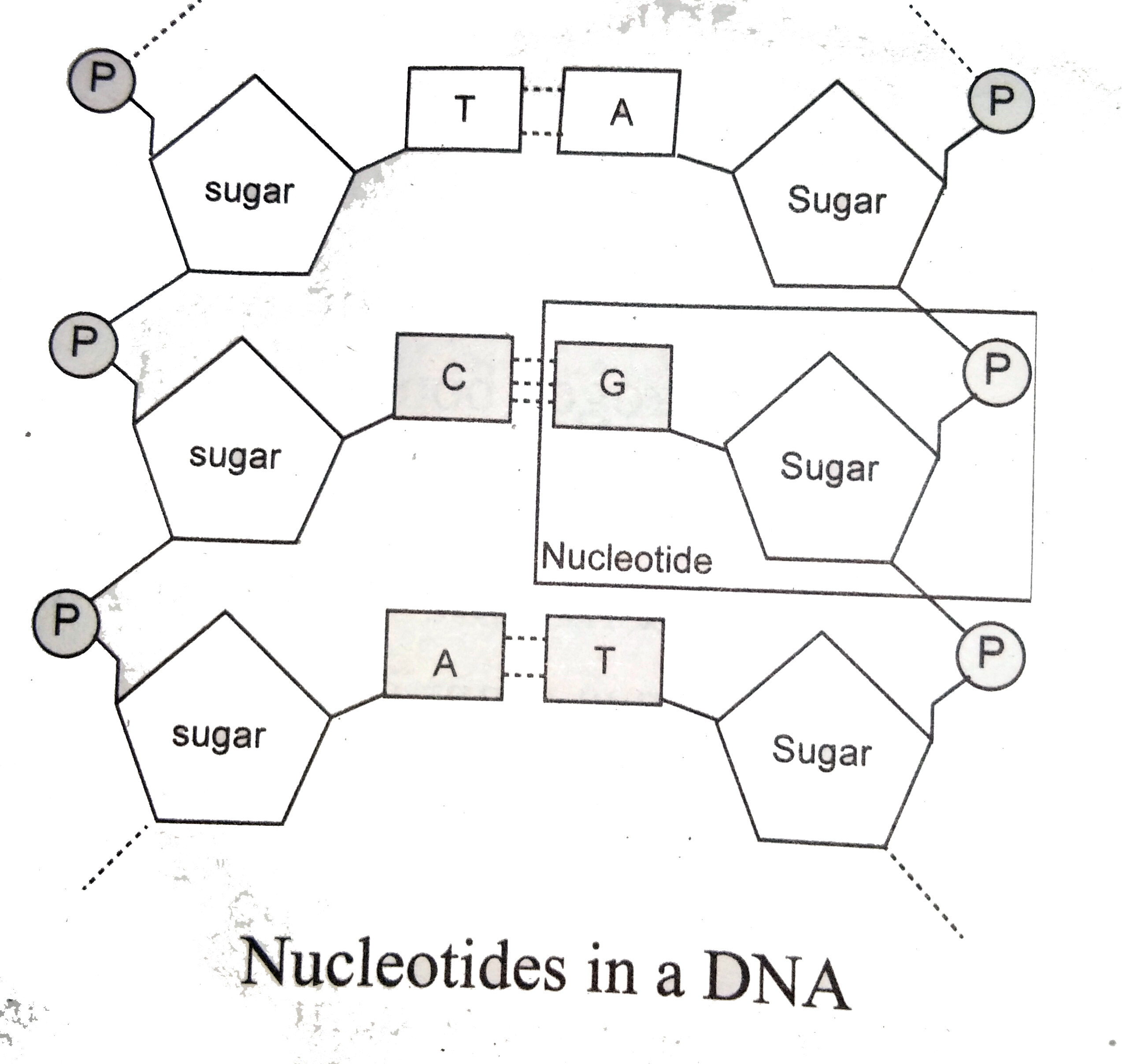
41 label of nucleotide
Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 The labeled aha-dUTP and aha-dCTP nucleotides can be used to generate labeled nucleic acid hybridization probes for many molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including two-color microarray assays, northern and Southern blots, colony and plaque hybridizations, DNA sequencing, primer extension, DNA and RNA amplification and … 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Nucleotides in DNA and RNA Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Nitrogenous Base Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines.
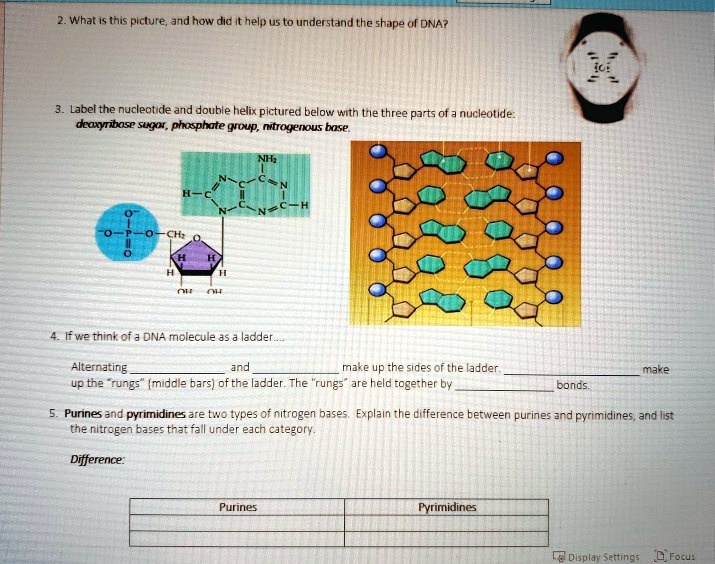
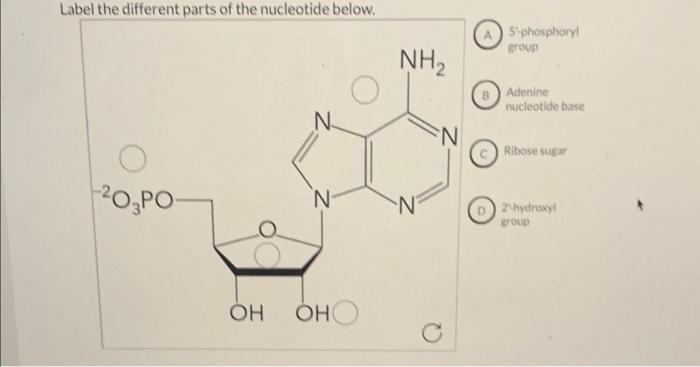
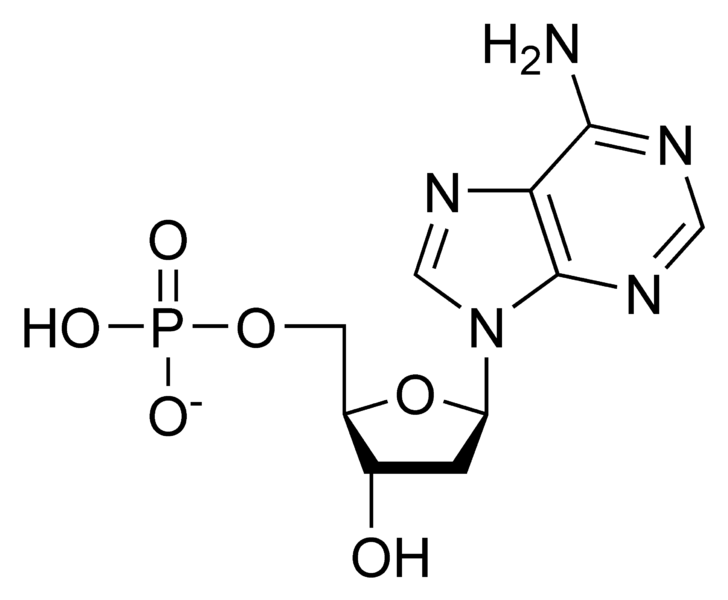
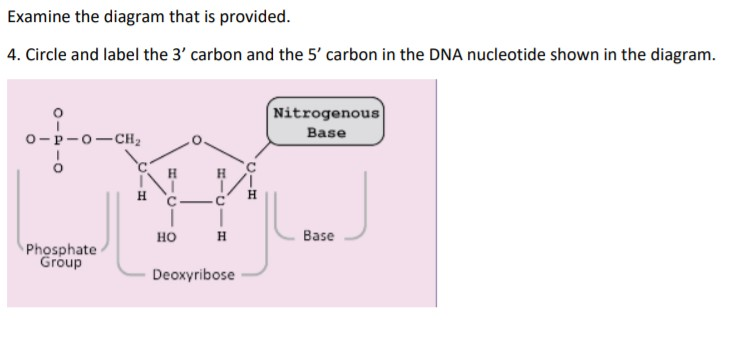
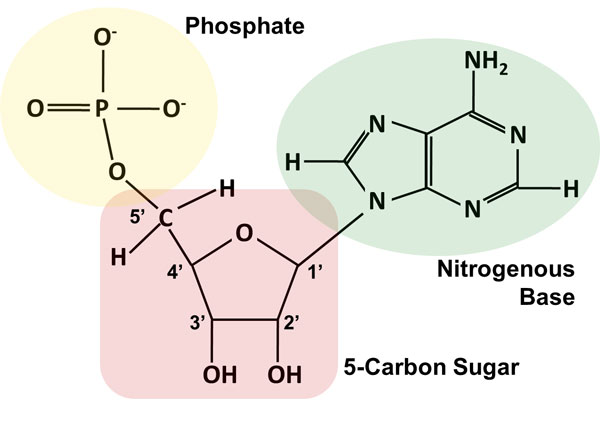
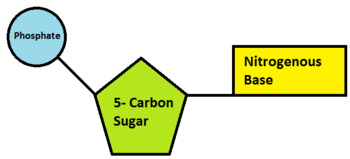
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? - Toppr The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group; 5-carbon sugar, and; nitrogenous base. · phosphate group · 5-carbon sugar, and ...
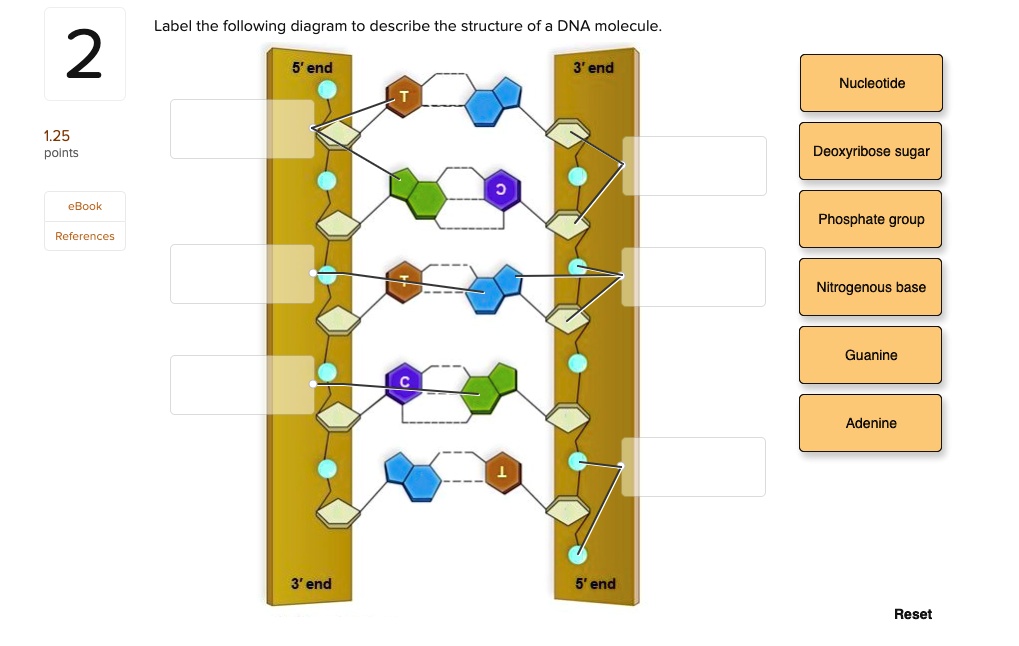
Label of nucleotide
Draw and label a Nucleotide | A Level Biology - YouTube Draw and label a Nucleotide | A Level BiologyCan you draw and label a nucleotide? This short clip is taken from the lesson "Nucleotides & Polynucleotides" AN... Nucleotide - Wikipedia Nucleotides are organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. DNA structure and replication review (article) | Khan Academy Nucleotide: Building block of nucleic acids: Double helix: Structure of two strands, intertwining around an axis like a twisted ladder: DNA replication: Process during which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules: Base pairing: Principle in which the nitrogenous bases of the DNA molecules bond with one ...
Label of nucleotide. Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram - Science Trends Nucleotides are molecules which serve as the building blocks, or monomer units, for the creation of important polymers like ribonucleic acid or RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. As mentioned, nucleotides have three component parts: a five-sided carbon sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group. Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJU'S Nucleotides are named as Adenylic acid, Guanylic acid, Thymidylic acid, Cytidylic acid and Uridylic acid. Nucleotides are also named as nucleoside mono, di or triphosphate, based on the number of phosphate groups attached to it, e.g. Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy All four nucleotides (A, T, G and C) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. It's a cyclical molecule—most of its atoms are arranged in a ring-structure. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides To radioactively label a DNA fragment for use as a probe, one of the incorporated nucleotides provided in the reaction is radiolabeled on the alpha ...
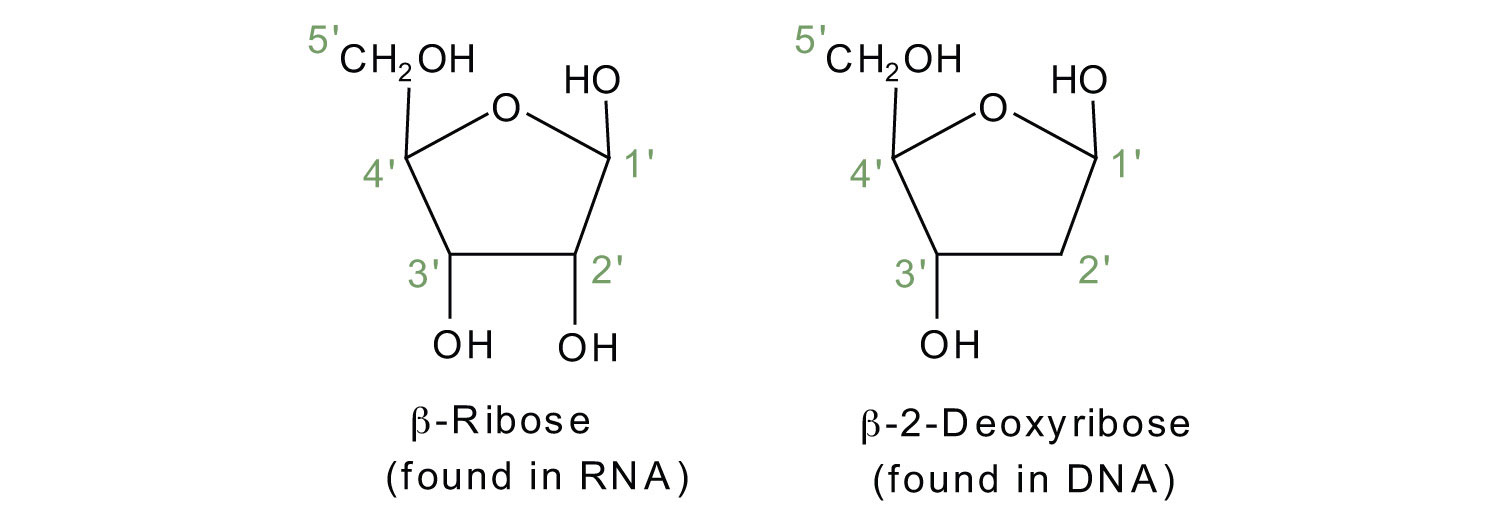
2.6: DNA and RNA Flashcards | Quizlet A nucleotide has three component parts: 1. a nitrogenous base 2. A 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) 3. A phosphate group Identify and label carbons by number (for example, C1, C2, C3) on a nucleotide drawing. Understanding: The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides. Nucleotides are organic molecules that act as the building blocks of both DNA and RNA. These molecules have three components - a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases are of two types - purines and pyrimidines. The purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G), while the pyrimidines are cytosine (C ... How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? It is a kind of biomolecule. The combination of a nucleoside molecule and a phosphate group leads to the formation of a nucleotide molecule. Answer and ... Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Common labels used to generate nucleic acid probes include radioactive phosphates, biotin, fluorophores and enzymes. In addition, the bioconjugation methods used for nucleic acid probe generation may be adapted for attaching nucleic acids to other molecules or surfaces to facilitate targeted delivery or immobilization, respectively. Page contents
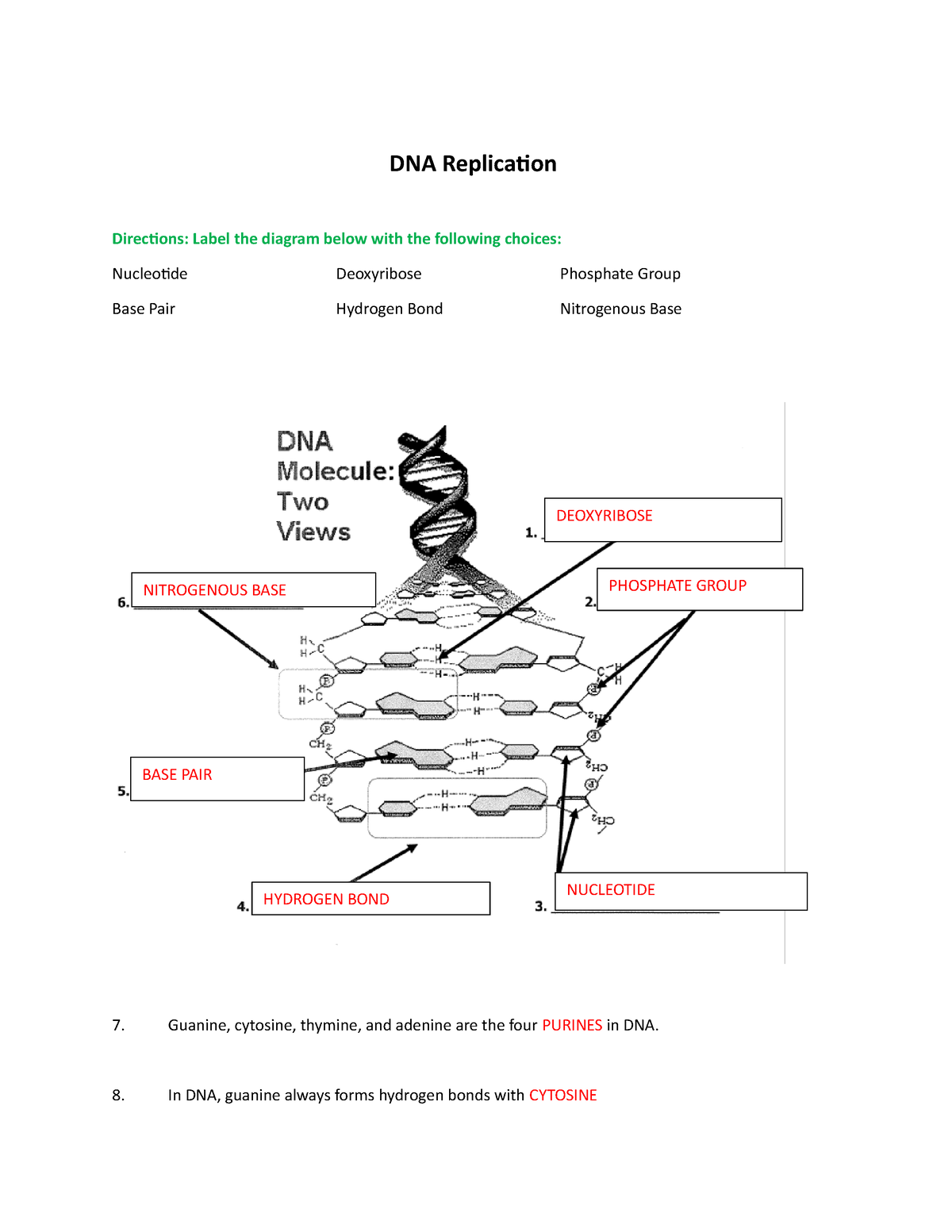
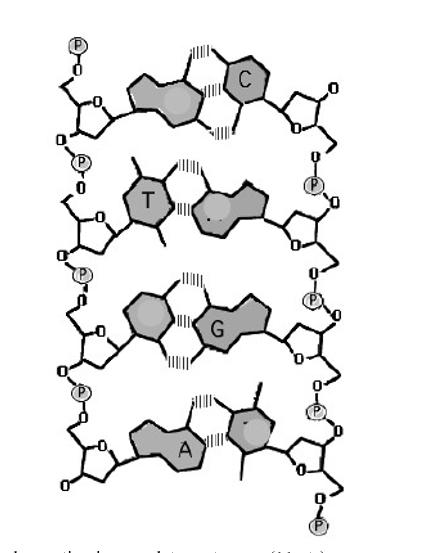
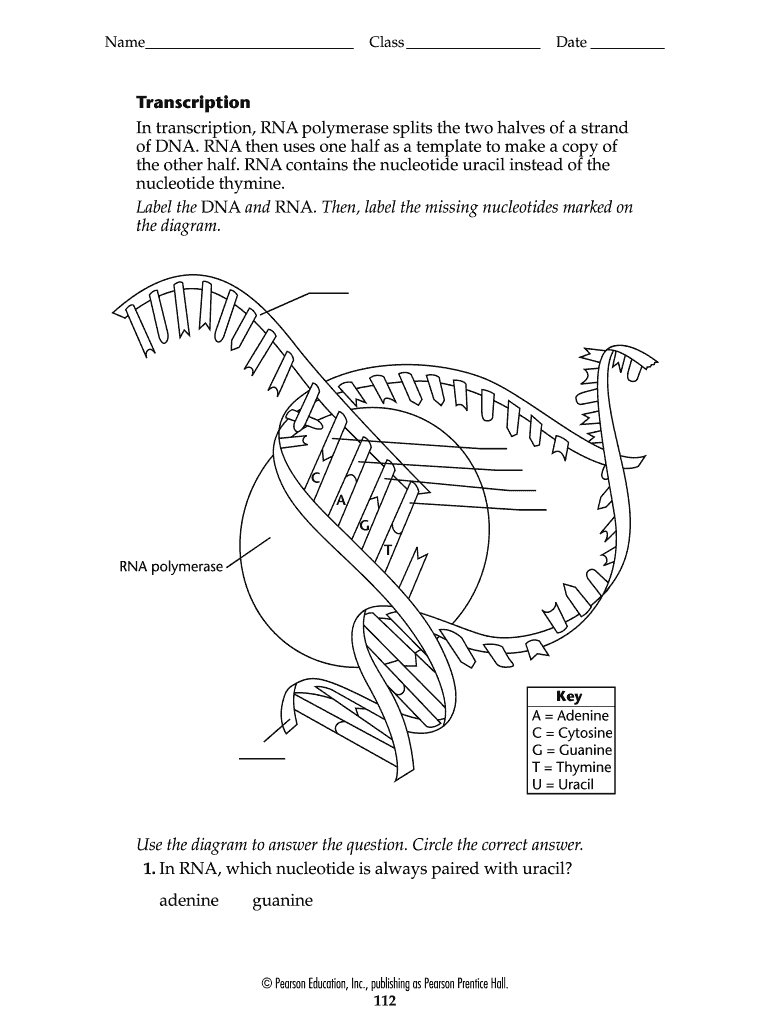
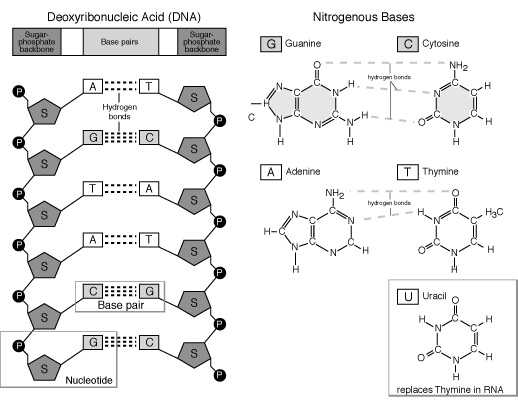
dna-labeling | NEB DNA Labeling. Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end ... 9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology | OpenStax Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base ( Figure 9.3 ). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA. How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic ... - Vedantu Apr 1, 2023 ... Guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine are the four nucleobases of DNA; uracil replaces thymine in RNA. Nucleotides are also integrated into ... 9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands.
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Biology Molecular Biology Basics Nucleic Acids 1 Answer Maxwell Jul 19, 2017 See below Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group 5-carbon sugar, and nitrogenous base. Answer link
DNA Labeling - NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified ...
Nucleotide - Genome A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine.
DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides - PerkinElmer Probe labeling process radioactively label the DNA & RNA fragments for detection or purification. These Radiolabeled nucleotides are typically incorporated enzymatically into specific nucleic acid sequences for detection and analysis.
Nucleic Acid Labeling - Sepmag Dec 16, 2021 ... Nucleic acids refer to biomolecules composed of nucleotides. A nucleotide is the name of a nucleic acid monomer which consists of a 5-carbon ...
Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Nucleotides are the biological molecules that serve as the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They are essential for all the functions performed by a living cell. Not only this, but they are also essential for transferring information to new cells or the next generation of the living organisms.
Cryo-EM structures of mitochondrial ABC transporter ABCB10 in apo and ... Structures of ABCB10-apo and ABCB10-BV. ABCB10-apo forms an inverted V-shape homodimer structure from the side view via the TMDs and each protomer is similar to that of ABCB10 in nucleotide-free ...
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
DNA structure and replication review (article) | Khan Academy Nucleotide: Building block of nucleic acids: Double helix: Structure of two strands, intertwining around an axis like a twisted ladder: DNA replication: Process during which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules: Base pairing: Principle in which the nitrogenous bases of the DNA molecules bond with one ...
Nucleotide - Wikipedia Nucleotides are organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth.
Draw and label a Nucleotide | A Level Biology - YouTube Draw and label a Nucleotide | A Level BiologyCan you draw and label a nucleotide? This short clip is taken from the lesson "Nucleotides & Polynucleotides" AN...










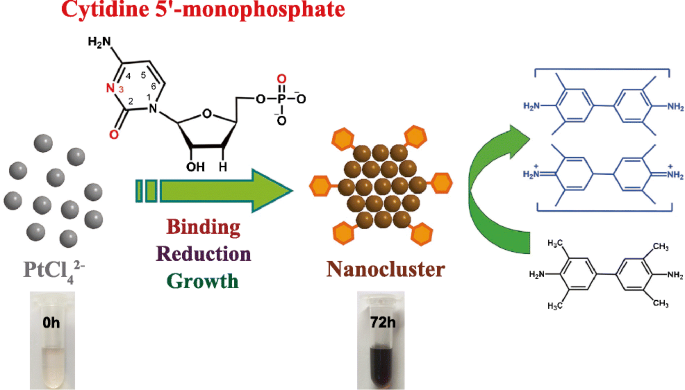


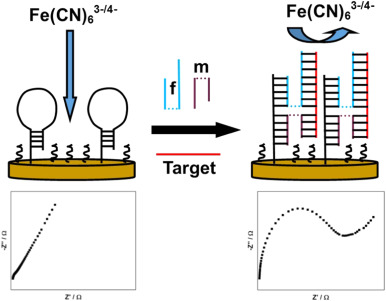





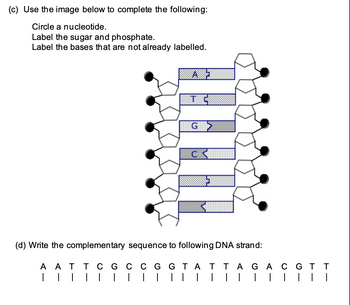
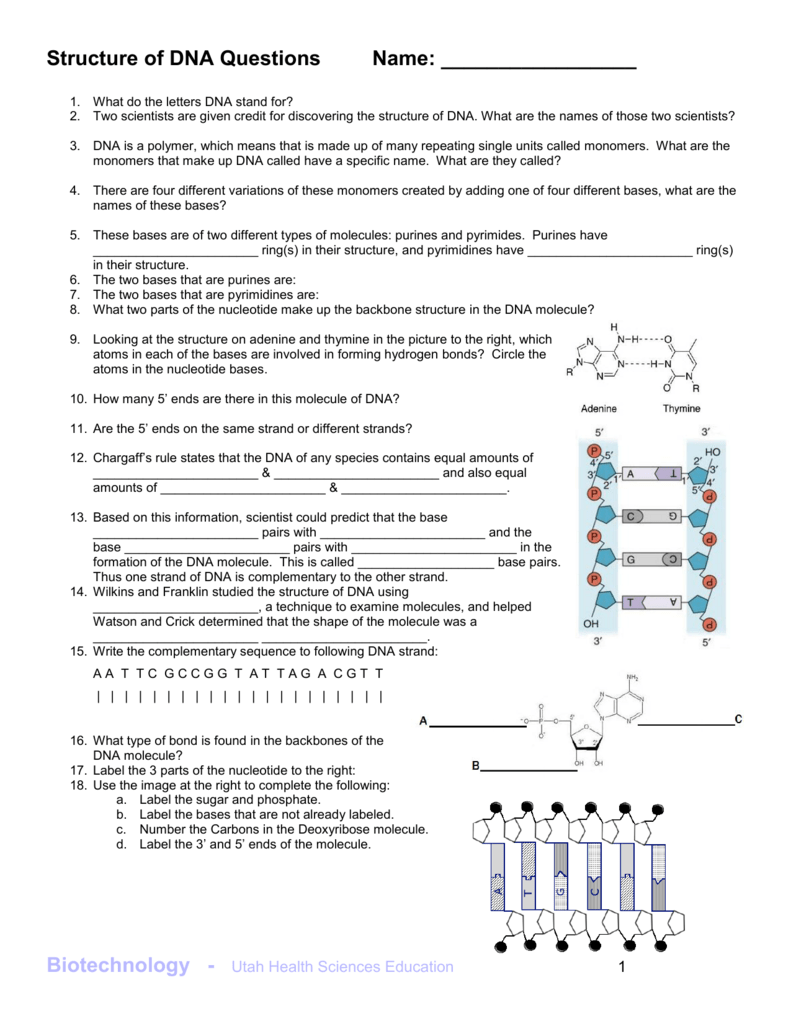



Post a Comment for "41 label of nucleotide"