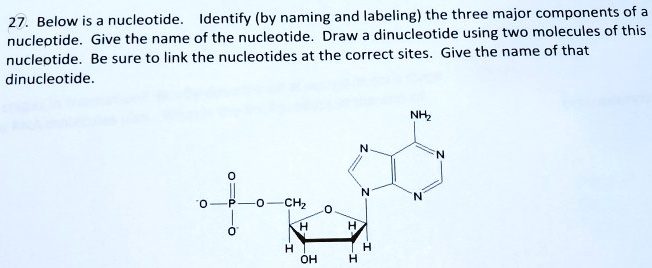
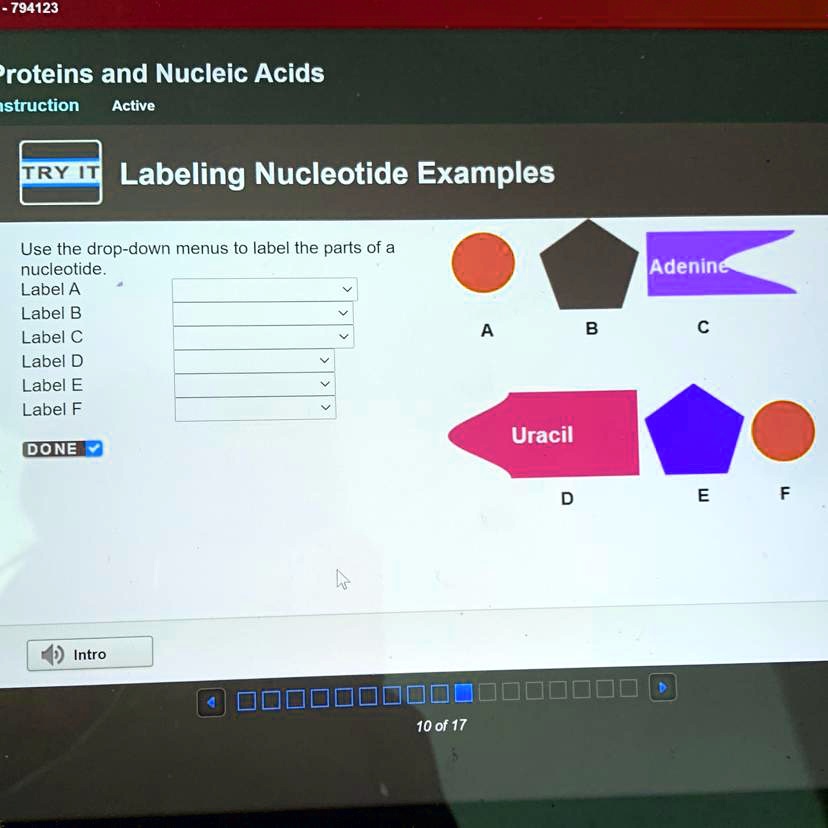
43 labeling nucleotide
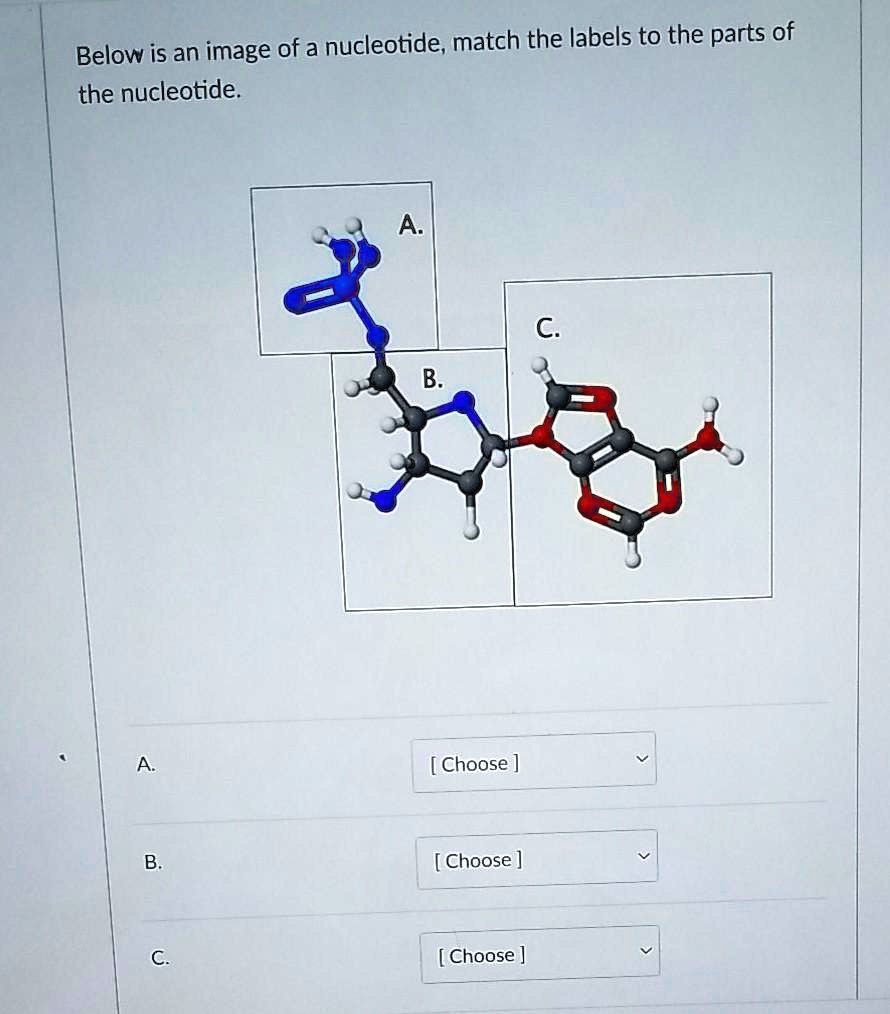
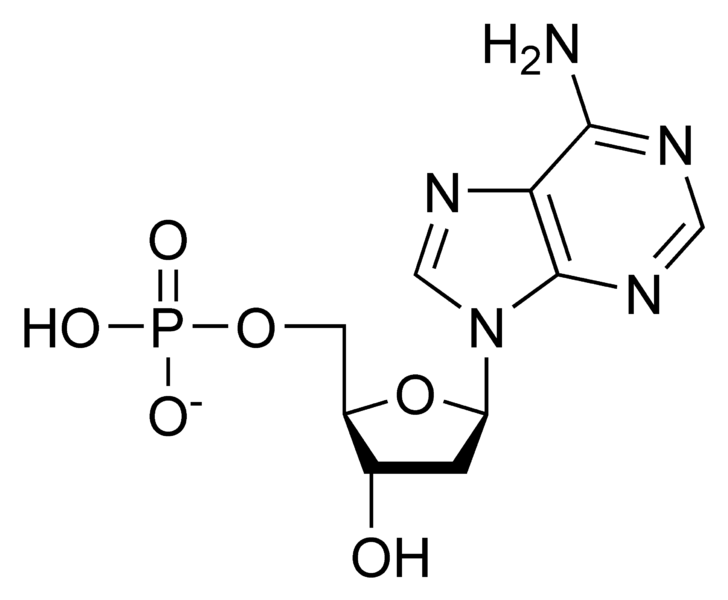
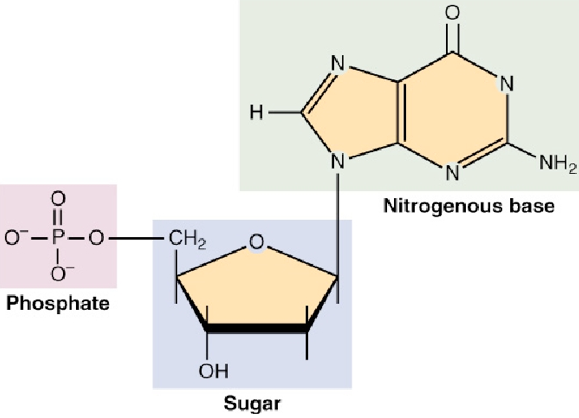
Digoxigenin - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The digoxigenin -anti-digoxigenin labeling system uses digoxigenin (DIG), a cardenolide steroid isolated from Digitalis plants (Martin et al., 1990). A nucleotide triphosphate analog containing the digoxigenin moiety (Figure 3.3) is incorporated into DNA by nick translation or random primer labeling.The DIG-labeled probe is detected by an enzyme-linked immunoassay using an antibody to ... How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Biology Molecular Biology Basics Nucleic Acids 1 Answer Maxwell Jul 19, 2017 See below Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group 5-carbon sugar, and nitrogenous base. Answer link
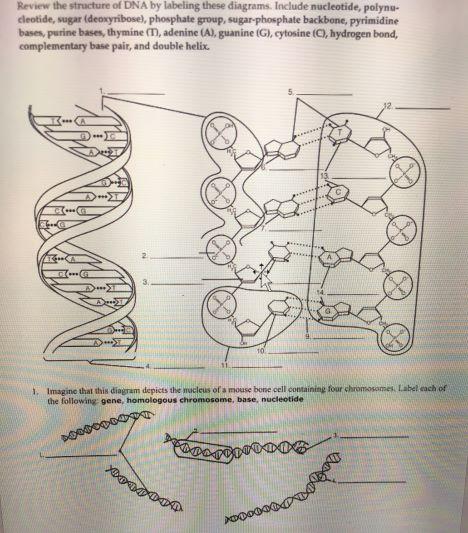
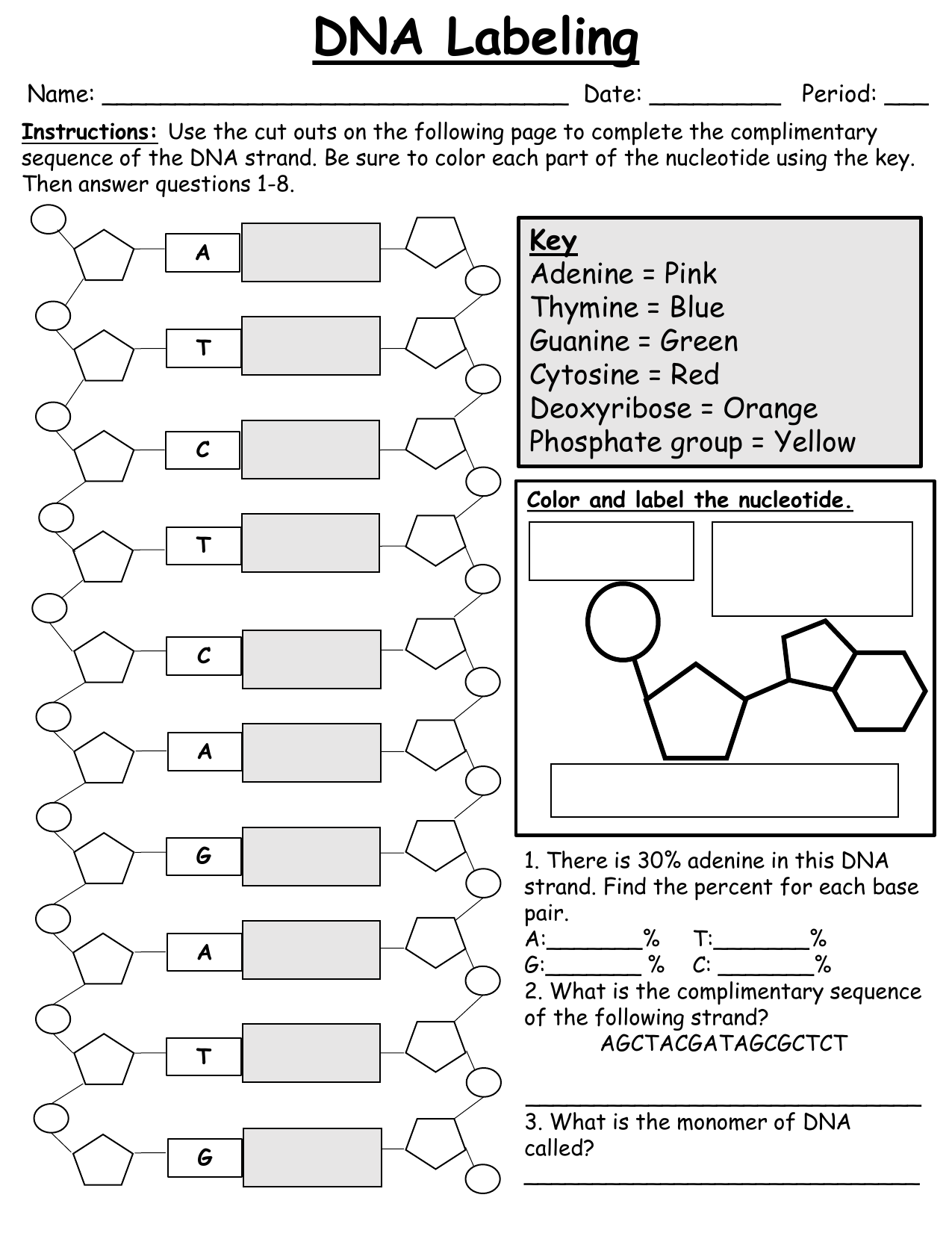
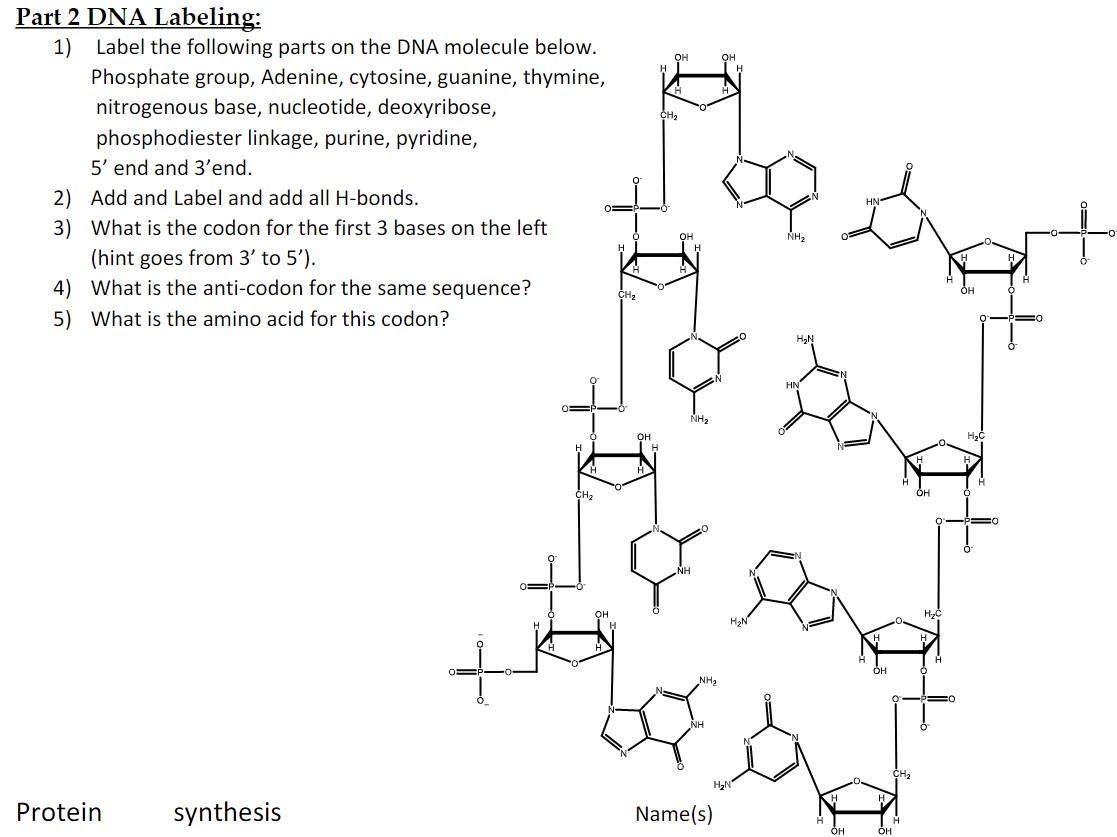
13. Label the nucleotides (A, T, G, C) in the DNA molecule below: The labeling of nucleotides (A, T, G, C) in the DNA molecule is as follows: Given that, A, T, G, C It stands for A = Adenine T = Thymine G = Guanine C = Cytosine Learn more: brainly.com/question/3617478?referrer=searchResults Advertisement ericp6905 Answer: A, T, G, C Explanation: A = Adenine T = Thymine G = Guanine C = Cytosine Advertisement

Labeling nucleotide
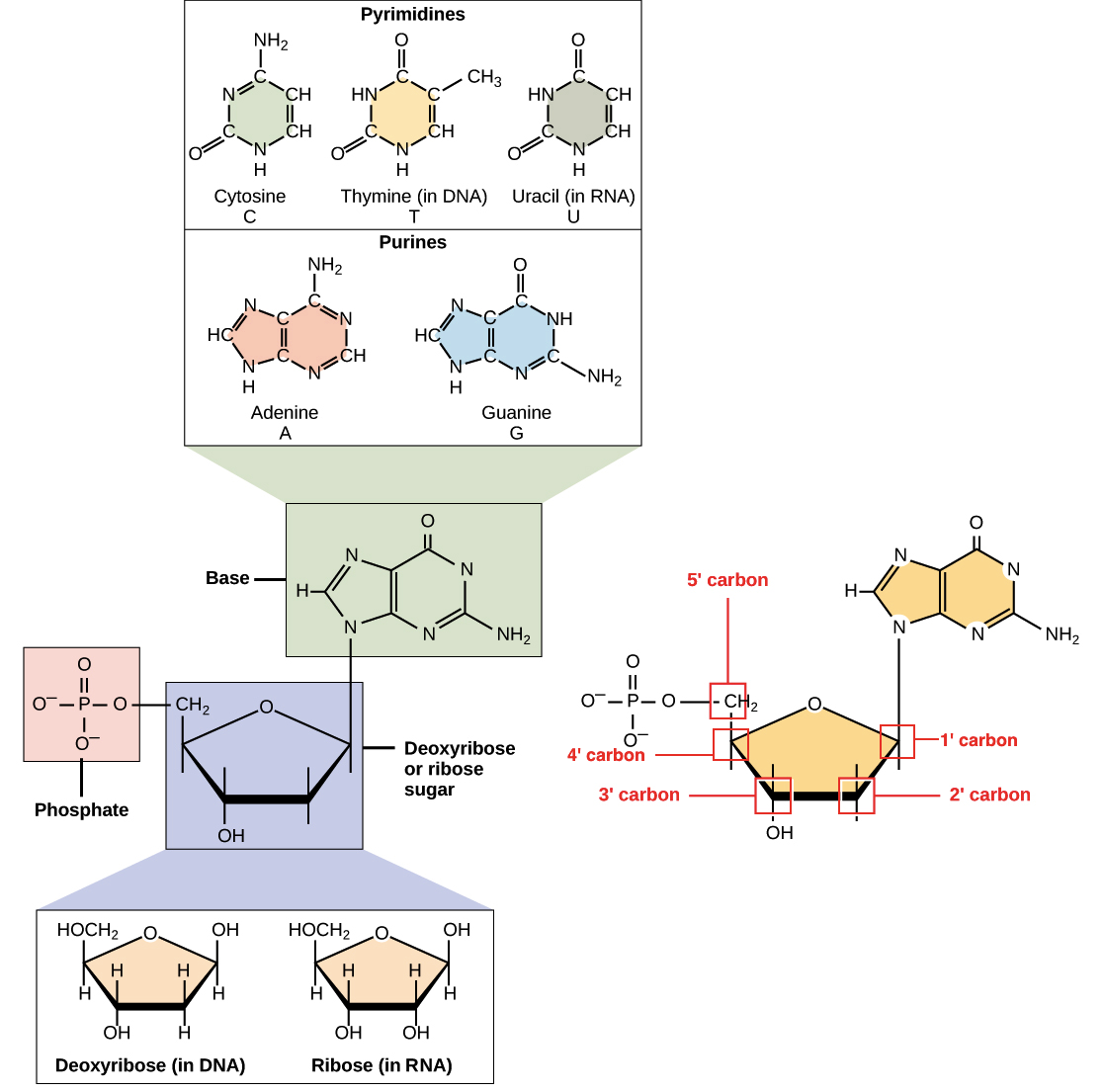
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. US6338943B1 - Methods for labeling nucleotides, labeled ... - Google The present invention provides improved methods for labeling nucleotides. The method of the invention for labeling nucleotides comprises the steps of: reacting a reactive moiety of a linker, which linker is a platinum compound having a stabilizing bridge and two reactive moieties, with an electron donating moiety of a spacer, which spacer comprises a chain having at least four atoms and at ... A Step toward Amino Acid-Labeled DNA Sequencing: Boosting Transmission ... In this theoretical report, the first-principles density functional theory calculations have been employed to study the role of three different labels, tyrosine (Tyr), aspartic acid (Asp), and arginine (Arg), for labeling DNA nucleotides and study their effect in rapid and controlled DNA sequencing at atomic resolution.
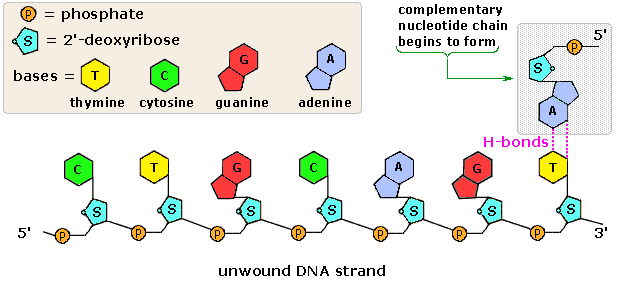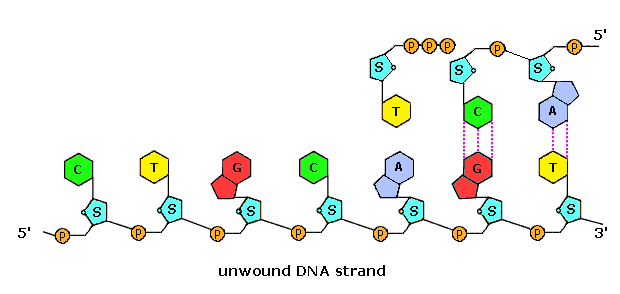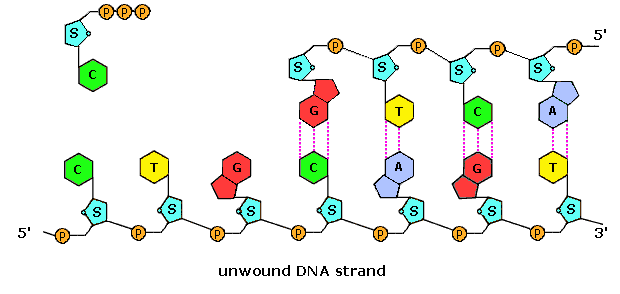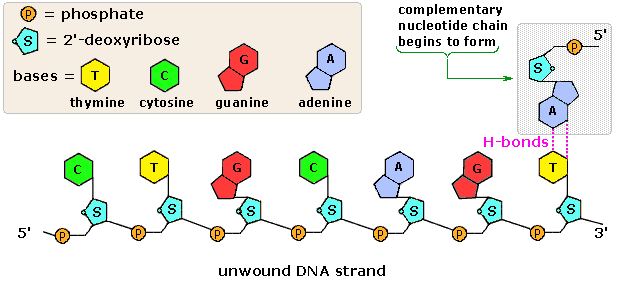
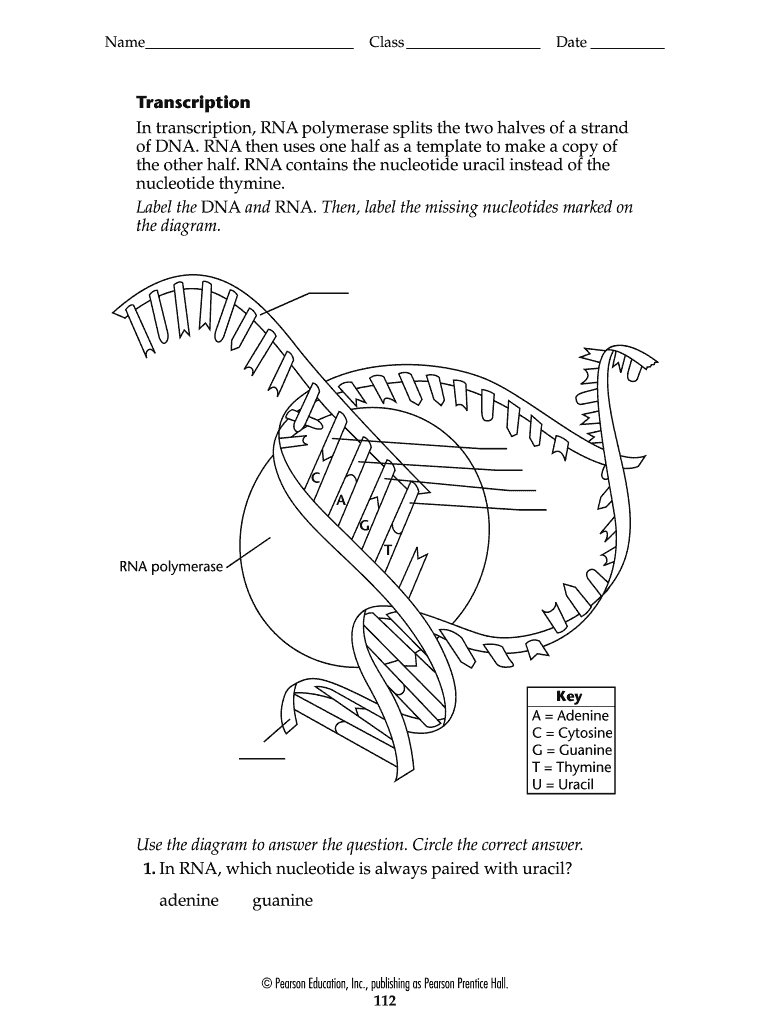
Labeling nucleotide. How to Label a DNA Structure | Sciencing Label your model paring half of the rung with an A, C, T, or G and its appropriate pair. Label the gap. Between the lettered rungs there is a gap. That gap is called the hydrogen bond. On your DNA molecule model or paper, point out and label the hydrogen bond. 00:00 00:00 An unknown error has occurred Brought to you by Sciencing Name the frame. DNA Molecule Label Diagram | Quizlet Nucleotide in a nucleic-acid chain, a sub-unit that consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base Cytosine The base that pairs with Guanine with DNA Base Pair A pair of complementary nitrogenous bases in a DNA molecule Hydrogen Bonds Bond holding together Nitrogen Bases in DNA Sugar-Phosphate Backbone Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 These ChromaTide nucleotides are useful for generating labeled nucleic acids for molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including chromosome and mRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) experiments ( ), gene expression and mutation detection on arrays and microarrays ( Figure 8.2.1 ), and in situ PCR and RT-PCR. Fluorescent Nucleotides for RNA Labeling - Jena Bioscience Fluorescent Nucleotides for RNA Labeling Nucleotide Selector for RNA Labeling Select a suitable nucleotide substrate for enzymatic RNA Labeling. Table 1: Enyzmatic incorporation of fluorescent Nucleotides. yPAP: Yeast Poly A Polymerase TdT: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase. 1: in-house tested 2: external reference (see datasheet)
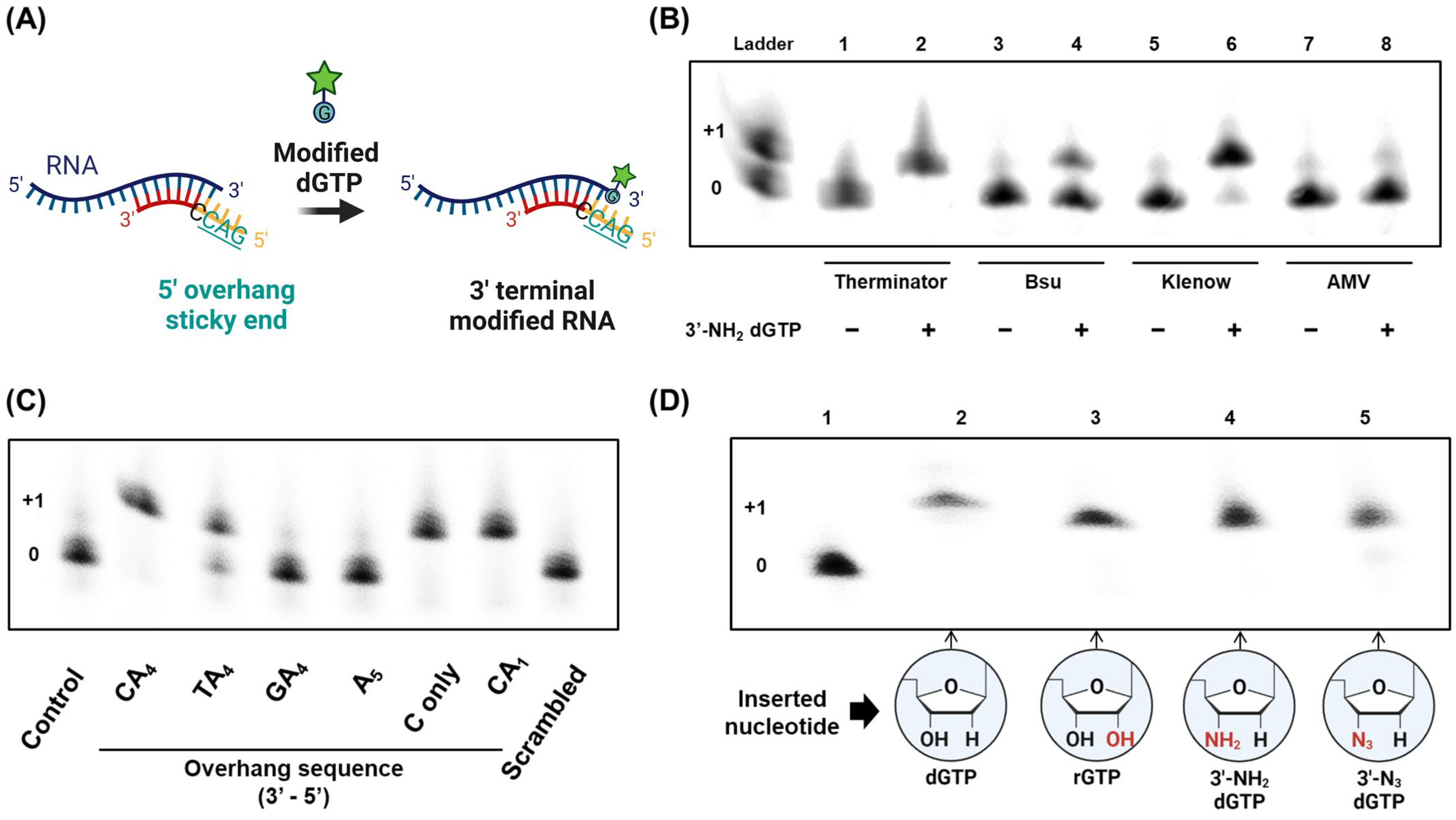
Incorporation of reporter-labeled nucleotides by DNA polymerases Nucleotide analogs are routinely used to label, isolate, study, and manipulate DNA in a wide variety of applications . These nonradioactive nucleotide analogs are introduced into a DNA strand by chemical and enzymatic 5′ and 3′ end labeling and through internal enzymatic labeling or post-labeling methods . Most methods however, replace only ... How (and Why) to Label Nucleic Acids - Bitesize Bio Generally speaking, there are two types of nucleic acid labeling techniques: radioisotope labeling and non-radioactive labeling. Radioisotope labeling: Considered as a conventional method for nucleic acid labeling, radiolabeled nucleotides are synthesized using ATP-gamma- 32 P or 35 P. How to Label a DNA Model | Sciencing A label identifying one nucleotide should clearly show the three connected molecules as a group. Arrows, strings or identifying markers like matching star stickers could be used to connect the three parts of the nucleotide to the label. Cite this Article Did you find this page helpful? 👍 👎 How do you label nucleotide bases? - KnowledgeBurrow.com How do you label nucleotide bases? A DNA strand is made of four bases, classified with the letters A, C, T, and G. A stands for adenine (a purine); C stands for cytosine (a pyrimidine); G stands for Guanine (also a purine); and T represents Thymine (a pyrimidine). The "rules" are that C always pairs with G, and A always pairs with T.
Nucleic Acid Labeling & Detection - Sigma-Aldrich Various labeling methods are used to distribute the label throughout the probe, including PCR with labeled deoxynucleotide (dNTPs) or nucleotide triphosphates (NTPs), random priming, and nick translation. End-labeling is particularly useful for assays investigating nucleic acid-protein interactions to avoid steric hindrance. Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Numerous reagents are available for quick and efficient benchtop oligonucleotide labeling, and they are most useful for making small amounts of probe or when many different probes with the same label are required (i.e., for mutational analysis). For small-scale probe generation needs, enzymatic methods are an economical method for labeling probes. Fluorescent Nucleotides for DNA Labeling - Jena Bioscience Table 1: Enzymatic incorporation of fluorescent Nucleotides. PCR: Polymerase chain reaction with Taq Polymerase; MDA-based WGA: Multiple displacement amplification (MDA)-based whole genome amplification (WGA) with Phi29 DNA Polymerase; NT: Nick Translation with DNAse I / DNA Polymerase I; Labeled Nucleotides - Biotium Labeled Nucleotides - Biotium Antibody Finder 0 Product Catalog Fluorescent Proteins, Nucleotides & Other Conjugates Amyloid & Neurodegeneration Stains Cell Cycle Analysis Chromogenic Substrates Equipment Fluorescence Microscopy HRP & Alkaline Phosphatase Conjugates Nucleic Acid Quantitation & Extraction Super-Resolution Imaging
dna-labeling | NEB DNA Labeling Product Listing Product Overview Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example.
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram - Science Trends Nucleotides are molecules which serve as the building blocks, or monomer units, for the creation of important polymers like ribonucleic acid or RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. As mentioned, nucleotides have three component parts: a five-sided carbon sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group.
A Step toward Amino Acid-Labeled DNA Sequencing: Boosting Transmission ... In this theoretical report, the first-principles density functional theory calculations have been employed to study the role of three different labels, tyrosine (Tyr), aspartic acid (Asp), and arginine (Arg), for labeling DNA nucleotides and study their effect in rapid and controlled DNA sequencing at atomic resolution.
US6338943B1 - Methods for labeling nucleotides, labeled ... - Google The present invention provides improved methods for labeling nucleotides. The method of the invention for labeling nucleotides comprises the steps of: reacting a reactive moiety of a linker, which linker is a platinum compound having a stabilizing bridge and two reactive moieties, with an electron donating moiety of a spacer, which spacer comprises a chain having at least four atoms and at ...
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.























Post a Comment for "43 labeling nucleotide"