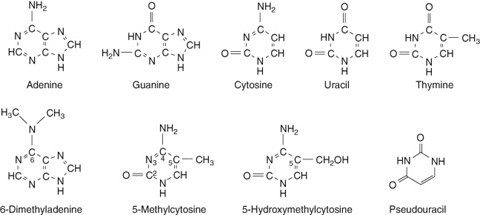
38 nitrogenous bases
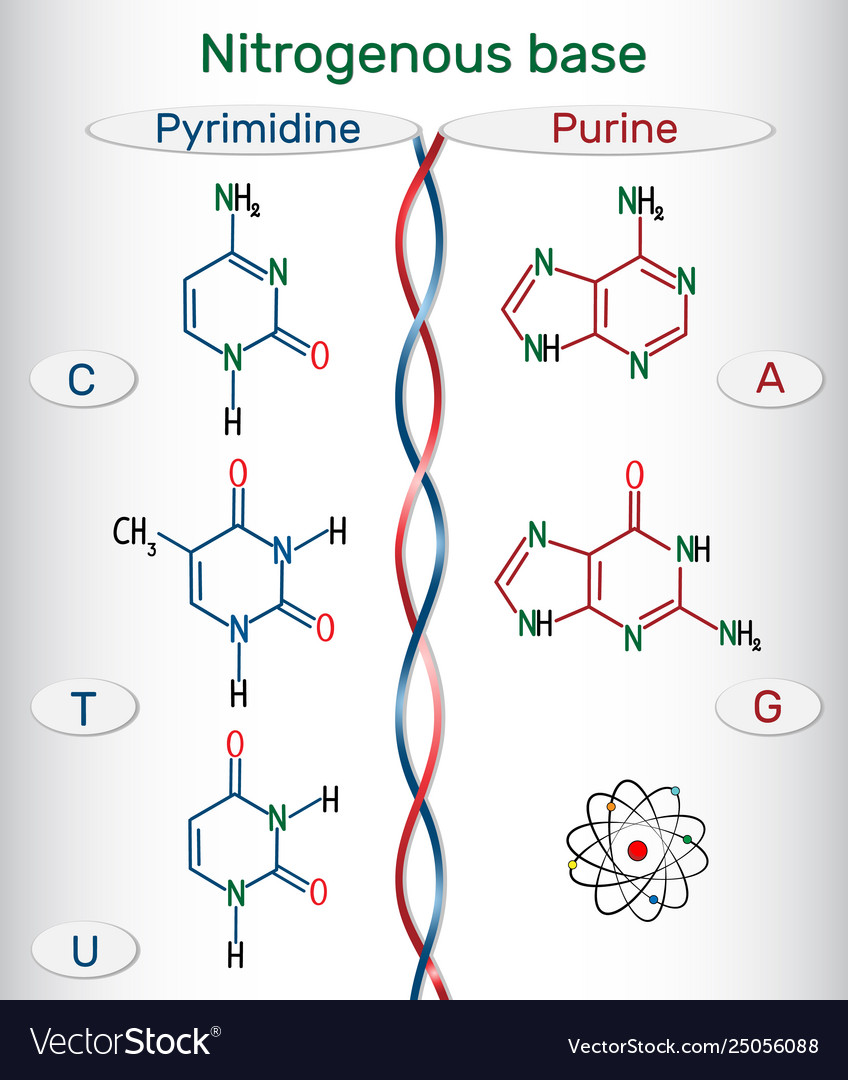
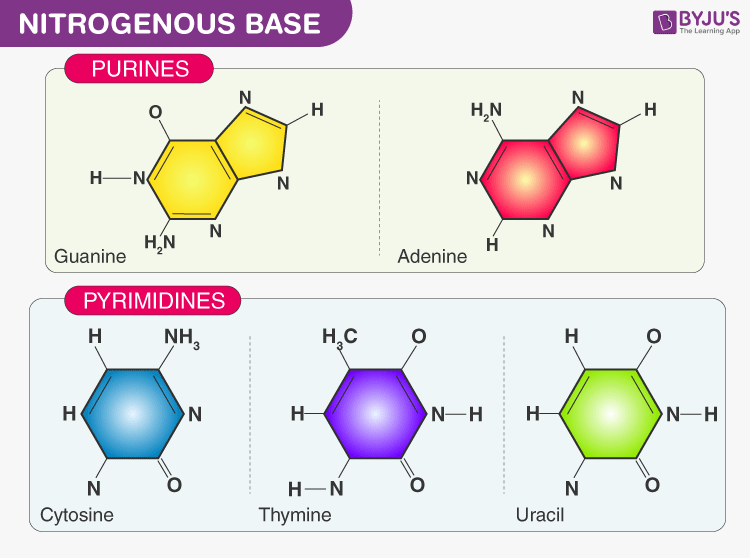
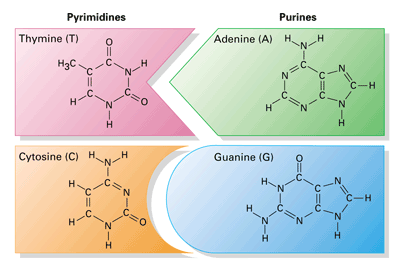
Nitrogenous Base - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Nucleotides Nucleotides include: (1) a nitrogenous base, (2) a five-carbon monosaccharide (aldopentose), and (3) phosphoric acid. Nitrogenous bases. Nucleotide hydrolysis produces two types of substances derived from the heterocyclic rings purine and pyrimidine known as the purine and pyrimidine bases. Nitrogenous Bases | BioNinja Nitrogenous Bases. Nucleic acids are composed of a combination of 5 nitrogenous bases: Guanine and adenine are double-ringed purine molecules. Cytosine, thymine and uracil are single-ringed pyrimidine molecules. Thymine and uracil are chemically similar molecules - thymine is present in DNA, while uracil is used in RNA.
When a nitrogenous base? Explained by FAQ Blog What are nitrogenous bases state their types? Nitrogenous bases are split into two different types: the purines (adenine and guanine) and the pyrimidines (thymine, cytosine, and uracil). A purine will hydrogen-bond to a pyrimidine. Adenine always bonds with thymine (in DNA ) or with uracil (in RNA ) with two hydrogen bonds.

Nitrogenous bases
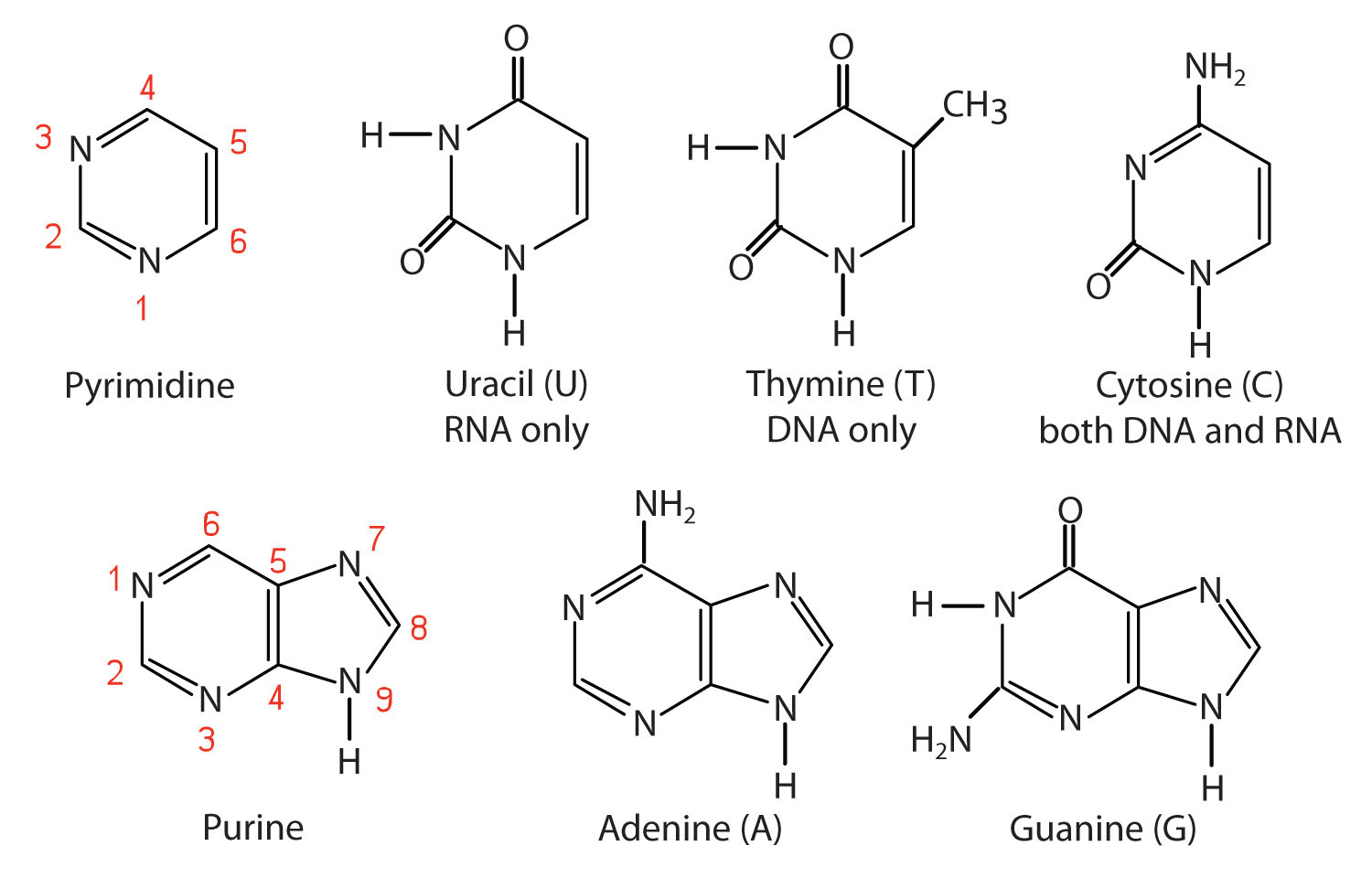
Nitrogenous bases | definition of Nitrogenous bases by Medical dictionary base. [ bās] 1. the lowest part or foundation of anything. See also basis. 2. the main ingredient of a compound. 3. the nonacid part of a salt; a substance that combines with acids to form salts. In the chemical processes of the body, bases are essential to the maintenance of a normal acid-base balance. Excessive concentration of bases in the ... Nitrogenous Bases - Laboratory Notes Nitrogenous bases (also known as Nucleobases or bases) are nitrogen-containing compounds. They are an important component of nucleic acids. These bases together with ribose (sugar molecule) and phosphate form nucleotides, the monomeric unit of DNA and RNA. The following five nitrogenous bases are structural components of nucleic acids: Adenine (A) What Nitrogenous Bases Are Found in DNA? - BYJUS There are four different types of nitrogenous bases present in DNA. They are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C). Adenine and guanine are purine bases, whereas thymine and cytosine are pyrimidine bases. In a double stranded DNA, base pairing occurs between complementary bases of two strands.
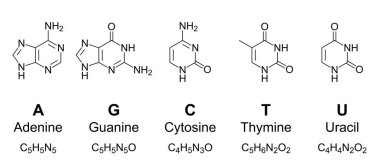
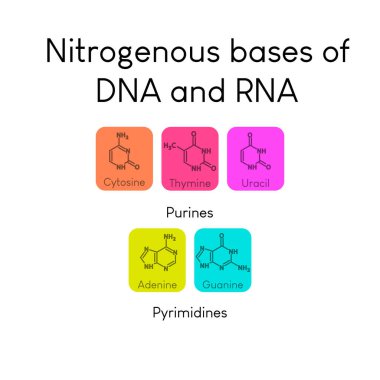
Nitrogenous bases. Nitrogenous Bases: Hydrogen Bonding, Overview - Study.com Nitrogenous Bases If you think of DNA as a twisted ladder, nitrogenous bases are the 'rungs.' They are shaped like flat rings stacked on top of each other in the middle of the DNA strand. Their... Medical Definition of Nitrogenous base - MedicineNet Nitrogenous base: A molecule that contains nitrogen and has the chemical properties of a base. The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). The nitrogenous bases in RNA are the same, with one exception: adenine (A), guanine (G), uracil (U), and cytosine (C). What are the nitrogenous bases of DNA and RNA? - Quora In DNA, the four Nitrogenous bases are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine whereas in RNA they are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uridine. Some modified bases are present in tRNAs. Sion Roberts 4 y Your nitrogenous bases are vital in DNA and RNA. Nitrogenous Bases in RNA Fig. 3: The Four Nitrogenous Bases in RNA: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil. Adenine and guanine are also known as purine bases; cytosine and uracil are also called pyrimidine bases. Each ribonucleotide will contain one of these four bases.
Nucleobase - Wikipedia Nucleobases, also known as nitrogenous bases or often simply bases, are nitrogen -containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. Nitrogenous Base - Definition, Explanation, Quiz | Biology Dictionary In DNA and RNA, a nitrogenous base forms a bond with a 5-sided carbon sugar molecule, which forms a "backbone" for the entire molecule. A nitrogenous base plus this sugar backbone is known as a nucleotide, and forms the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nitrogenous Base within Nucleic Acids Purines and Pyrimidines Nitrogenous base - The School of Biomedical Sciences Wiki The nitrogenous base is one of the three components of a nucleotide which in turn join up to form DNA. The three components of a nucleotide are a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous bas . References . ↑ Alberts, BA,Johnson, AJ,Lewis, JL, Raff,MR, Roberts, KR, Walters, PW. 2008. The Cell. Fifth Edition. 197-198. Nitrogen base Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com or nitrogenous base 📓 noun Chemistry, Biochemistry. a nitrogen-containing organic compound that has the chemical properties of a base, especially a pyrimidine or purine: Four nitrogen bases are present in a DNA molecule. Words nearby nitrogen base
Nitrogenous Bases - GSU Nitrogenous Bases. A set of five nitrogenous bases is used in the construction of nucleotides, which in turn build up the nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. These bases are crucially important because the sequencing of them in DNA and RNA is the way information is stored. The letters which form the codons in the genetic code are the A C U G of the ... Nitrogenous Bases Nitrogenous bases, also called nucleobases, are nitrogenous compounds that form an important part of the nucleotides. Nucleotides are building blocks of DNA and RNA that are composed of a sugar, nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. Medical Definition of Nitrogenous base - RxList The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), guanine ( G ), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). The nitrogenous bases in RNA are the same, with one exception: adenine (A), guanine (G), uracil (U), and cytosine (C). SLIDESHOW nitrogenous base | Encyclopedia.com nitrogenous baseA basic compound containing nitrogen. The term is used especially of organic ring compounds, such as adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine, which are constituents of nucleic acids. A Dictionary of Biology Cite this article Pick a style below, and copy the text for your bibliography. MLA Chicago APA "nitrogenous base
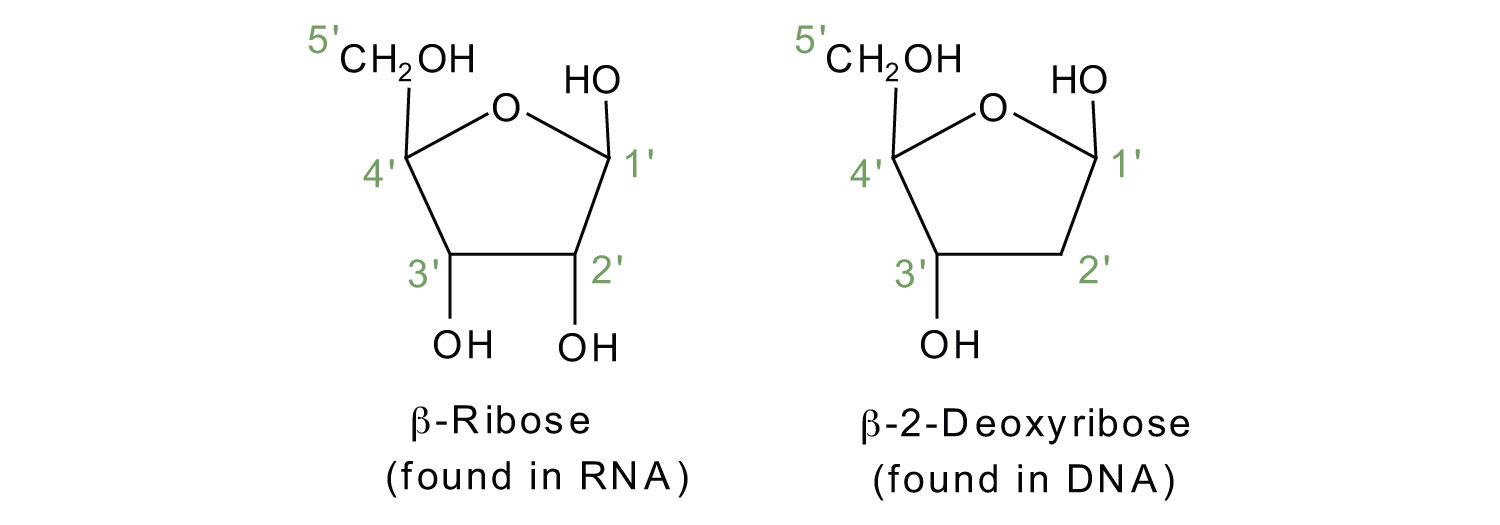
Sequence Of Nitrogenous Bases In RNA: What, Why, Purpose, Detailed Facts The five nitrogenous bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine and uracil. With the four nitrogenous bases in RNA are preferably adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. DNA has uracil replaced by thymine. The sugar ring of five carbons and the inside of the nitrogenous bases among both the RNA and DNA are a bit different from each other.
Nitrogenous Bases in DNA & RNA | What is a Nitrogen Base Pair? Nitrogenous bases are organic molecules that contain a ring structure that includes both carbon and nitrogen atoms and can act as a base in chemical reactions. The lone pair of electrons on one of...
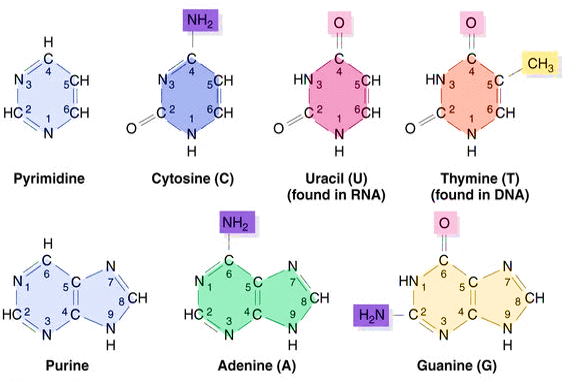
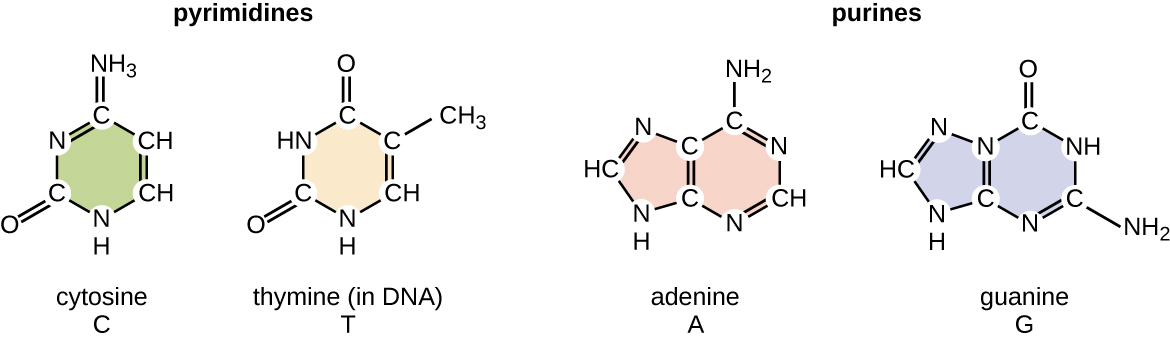
Nitrogenous Bases - Biochemistry - Varsity Tutors In DNA and RNA, there are two types of nitrogenous bases: pyrimidines and purines. A pyrimidine contains one carbon-nitrogen ring with two nitrogen atoms. A purine consists of a pyrimidine fused with an imidazole ring. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. Report an Error
Types of Nitrogenous Bases In RNA: Detailed Facts The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. RNA also has same types of nitrogenous bases yet with one only exception which is the uracil is there instead of thymine. The nitrogen have biological related material with complements of nitrogenous.
Nitrogen bases: classification and functions - science - 2022 In other words, nitrogenous bases are a part of the units that make up nucleic acids (RNA and DNA) and the other molecules mentioned. There are two main groups of nitrogenous bases: purine or purine bases and pyrimidine or pyrimidine bases. The first group includes adenine and guanine, while thymine, cytosine, and uracil are pyrimidine bases.
Nitrogenous Bases Flashcards | Quizlet nitrogenous bases that have a single ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms, such as cytosine, uracil, and thymine. Related questions. QUESTION. S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) is an organic molecule bound to various metabolic enzyme and functions transfer methyl groups from SAM to an acceptor. What is the proper designation of SAM?
What Nitrogenous Bases Are Found in DNA? - BYJUS There are four different types of nitrogenous bases present in DNA. They are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C). Adenine and guanine are purine bases, whereas thymine and cytosine are pyrimidine bases. In a double stranded DNA, base pairing occurs between complementary bases of two strands.
Nitrogenous Bases - Laboratory Notes Nitrogenous bases (also known as Nucleobases or bases) are nitrogen-containing compounds. They are an important component of nucleic acids. These bases together with ribose (sugar molecule) and phosphate form nucleotides, the monomeric unit of DNA and RNA. The following five nitrogenous bases are structural components of nucleic acids: Adenine (A)
Nitrogenous bases | definition of Nitrogenous bases by Medical dictionary base. [ bās] 1. the lowest part or foundation of anything. See also basis. 2. the main ingredient of a compound. 3. the nonacid part of a salt; a substance that combines with acids to form salts. In the chemical processes of the body, bases are essential to the maintenance of a normal acid-base balance. Excessive concentration of bases in the ...





/purine-and-pyrimidine-nitrogenous-bases---skeletal-chemical-formulas-475632152-d34de0fec4e14f108a3e32901a1386c8.jpg)















Post a Comment for "38 nitrogenous bases"